
Once a stream cipher makes a key, the encryption and decryption process is almost instantaneous. Speed of encryption tops the list of advantages for stream ciphers. The advantages and disadvantages of using a stream cipher A stream cipher is a type of symmetric, as opposed to asymmetric, encryption. Stream ciphers users should not use the same IV more than once, however, to maximize the security of this process. This time, instead of the data and keystream being XOR-ed, the ciphertext and the keystream are XOR-ed. Once each bit of data has been XOR-ed by the stream cipher, it will produce an unreadable ciphertext message.ĭecryption of the ciphertext can happen in a manner similar to how the plaintext encryption occurs. This is part of what makes stream cipher encryption so fast. If the two are different - i.e., a combination of 1 and 0 - the XOR operator will produce a 1. If the two digits are the same, the XOR operator will produce a zero. It generates these values by comparing bits in the plaintext and the keystream that share the same position.įor example, the first bit in Person A's 10-bit message will be XOR-ed with the first bit of the keystream.

The XOR operator creates new binary values, which make up the ciphertext. Lower-end cryptographic number generators can sometimes have patterns that malicious users, or hackers, can identify and use to decrypt the ciphertext.Īfter the user has created the keystream, the stream cipher combines the keystream with the corresponding digits of the plaintext using the exclusive-or ( XOR) operator.
#Cipher definition generator
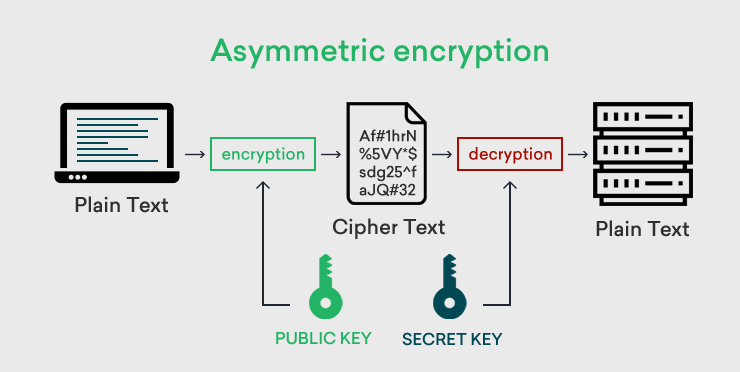
The quality of the number generator contributes to the randomness and security of the ciphertext, however. Placing this seed value into a cryptographic number generator, Person A can create a pseudo-random keystream that matches the size of their desired plaintext file. To do that, they must first use an initialization vector ( IV) to generate a random seed value. Here, Person A decides to use a 4-bit key to encrypt a 10-bit message. Furthermore, to avoid having to create a larger keystream, users can use a cryptographic number generator to create a larger keystream from a smaller, pseudo-random key. This is because Person A could opt to create a pseudo-random cipher digit stream, or keystream, using a key that is smaller than the size of the plaintext file. This can become cumbersome depending on the size of the message or document they are attempting to encrypt, however.Ĭryptographers also refer to the symmetric key used in a stream cipher as a keystream. The one-time pad, in this case, would also be at least 10 bits long. Here is an example to illustrate the one-timed pad process of stream ciphering: Person A attempts to encrypt a 10-bit message using a stream cipher. A stream cipher is a cryptographic cipher to convert (encrypt) text to produce ciphertext and back. Mathematically, a one-time pad is unbreakable because it's always at least the exact same size as the message it is encrypting. The key typically used with a stream cipher is known as a one-time pad. This makes for a fast and relatively simple encryption process.īasic encryption requires three main components: What makes stream ciphers particularly unique is that they encrypt data one bit, or byte, at a time. Asymmetric keys will sometimes use one key to encrypt a message and another to decrypt the respective ciphertext. A symmetric cipher key, as opposed to an asymmetric cipher key, is an encryption tool that is used in both encryption and decryption. How does a stream cipher work?Ī stream cipher is an encryption algorithm that uses a symmetric key to encrypt and decrypt a given amount of data. The main alternative method to stream cipher is, in fact, the block cipher, where a key and algorithm are applied to blocks of data rather than individual bits in a stream. A stream cipher is a method of encrypting text (to produce ciphertext) in which a cryptographic key and algorithm are applied to each binary digit in a data stream, one bit at a time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
